Make the016.com a preferred choice with Google by clicking here 
The microbes living in the gut are key to good health. Dr_Microbe/iStock/Getty Images Plus
Ana Maldonado-Contreras, University of Massachusetts Medical School
You may not know it, but you have an army of microbes living inside of you that are essential for fighting off threats, including the virus that causes COVID-19.
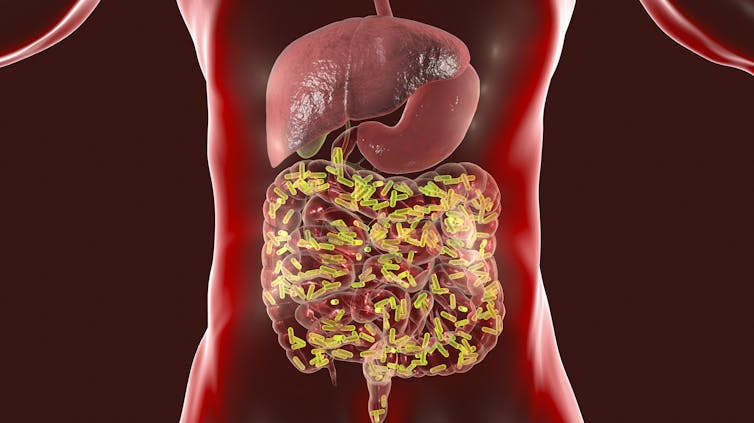
In the past two decades scientists have learned our bodies are home to more bacterial cells than human ones. This community of bacteria that lives in and on us – called the microbiome – resembles a company, with each microbe species performing specialized jobs but all working to keep us healthy. In the gut, the bacteria balance the immune response against pathogens. These bacteria ensure the immune response is effective but not so violent that it causes collateral damage to the host.
Bacteria in our guts can elicit an effective immune response against viruses that not only infect the gut, such as norovirus and rotavirus, but also those infecting the lungs, such as the flu virus. The beneficial gut microbes do this by ordering specialized immune cells to produce potent antiviral proteins that ultimately eliminate viral infections. And the body of a person lacking these beneficial gut bacteria won’t have as strong an immune response to invading viruses. As a result, infections might go unchecked, taking a toll on health.
I am a microbiologist fascinated by the ways bacteria shape human health. An important focus of my research is figuring out how the beneficial bacteria populating our guts combat disease and infection. My most recent work focuses on the link between a particular microbe and the severity of COVID-19 in patients. My ultimate goal is to figure out out how to enhance the gut microbiome with diet to evoke a strong immune response – for not just SARS-CoV-2 but all pathogens.
Good bacteria help the immune system ward off harmful microbes. chombosan/iStock/Getty Images Plus
Our immune defense is part of a complex biological response against harmful pathogens, such as viruses or bacteria. However, because our bodies are inhabited by trillions of mostly beneficial bacteria, virus and fungi, activation of our immune response is tightly regulated to distinguish between harmful and helpful microbes.
Our bacteria are spectacular companions diligently helping prime our immune system defenses to combat infections. A seminal study found that mice treated with antibiotics that eliminate bacteria in the gut exhibited an impaired immune response. These animals had low counts of virus-fighting white blood cells, weak antibody responses and poor production of a protein that is vital for combating viral infection and modulating the immune response.
In another study, mice were fed Lactobacillus bacteria, commonly used as probiotic in fermented food. These microbes reduced the severity of influenza infection. The Lactobacillus-treated mice did not lose weight and had only mild lung damage compared with untreated mice. Similarly, others have found that treatment of mice with Lactobacillus protects against different subtypes of influenza virus and human respiratory syncytial virus – the major cause of viral bronchiolitis and pneumonia in children.
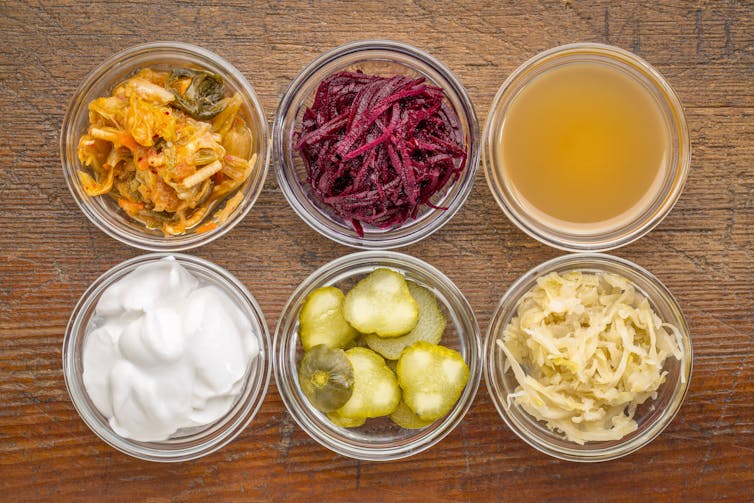

Fermented foods like kimchi, red beets, apple cider vinegar, coconut milk yogurt, cucumber pickles and sauerkraut can help provide beneficial bacteria. marekuliasz/iStock/Getty Images Plus
Patients with chronic illnesses including Type 2 diabetes, obesity and cardiovascular disease exhibit a hyperactive immune system that fails to recognize a harmless stimulus and is linked to an altered gut microbiome.
In these chronic diseases, the gut microbiome lacks bacteria that activate immune cells that block the response against harmless bacteria in our guts. Such alteration of the gut microbiome is also observed in babies delivered by cesarean section, individuals consuming a poor diet and the elderly.
In the U.S., 117 million individuals – about half the adult population – suffer from Type 2 diabetes, obesity, cardiovascular disease or a combination of them. That suggests that half of American adults carry a faulty microbiome army.
Research in my laboratory focuses on identifying gut bacteria that are critical for creating a balanced immune system, which fights life-threatening bacterial and viral infections, while tolerating the beneficial bacteria in and on us.
Given that diet affects the diversity of bacteria in the gut, my lab studies show how diet can be used as a therapy for chronic diseases. Using different foods, people can shift their gut microbiome to one that boosts a healthy immune response.
A fraction of patients infected with SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19 disease, develop severe complications that require hospitalization in intensive care units. What do many of those patients have in common? Old age and chronic diet-related diseases like obesity, Type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
Black and Latinx people are disproportionately affected by obesity, Type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease, all of which are linked to poor nutrition. Thus, it is not a coincidence that these groups have suffered more deaths from COVID-19 compared with whites. This is the case not only in the U.S. but also in Britain.

Minority communities continue to bear the brunt of the pandemic. Blake Nissen for The Boston Globe via Getty Images
The COVID-19 pandemic has inspired me to shift my research and explore the role of the gut microbiome in the overly aggressive immune response against SARS-CoV-2 infection.
My colleagues and I have hypothesized that critically ill SARS-CoV-2 patients with conditions like obesity, Type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease exhibit an altered gut microbiome that aggravates acute respiratory distress syndrome.
Acute respiratory distress syndrome, a life-threatening lung injury, in SARS-CoV-2 patients is thought to develop from a fatal overreaction of the immune response called a cytokine storm that causes an uncontrolled flood of immune cells into the lungs. In these patients, their own uncontrolled inflammatory immune response, rather than the virus itself, causes the severe lung injury and multiorgan failures that lead to death.
Several studies described in one recent review have identified an altered gut microbiome in patients with COVID-19. And some companies including Seres Therapeutics, 4d Pharma PLC, Evelo Biosciences, VEDANTA bioscience, and Finch Therapeutics have recently attracted investor attention for their work on therapies for diseases including cancer, depression and inflammatory bowel diseases.
Identification of specific bacteria within the microbiome that could predict COVID-19 severity is lacking.
To address this question, my colleagues and I recruited COVID-19 hospitalized patients with severe and moderate symptoms. We collected stool and saliva samples to determine whether bacteria within the gut and oral microbiome could predict COVID-19 severity. The identification of microbiome markers that can predict the clinical outcomes of COVID-19 disease is key to help prioritize patients needing urgent treatment.
We demonstrated, in a paper which has not yet been peer reviewed, that the composition of the gut microbiome is the strongest predictor of COVID-19 severity compared to patient’s clinical characteristics commonly used to do so. Specifically, we identified that the presence of a bacterium in the stool – called Enterococcus faecalis– was a robust predictor of COVID-19 severity. Not surprisingly, Enterococcus faecalis has been associated with chronic inflammation.
Enterococcus faecalis collected from feces can be grown outside of the body in clinical laboratories. Thus, an E. faecalis test might be a cost-effective, rapid and relatively easy way to identify patients who are likely to require more supportive care and therapeutic interventions to improve their chances of survival.
But it is not yet clear from our research what is the contribution of the altered microbiome in the immune response to SARS-CoV-2 infection. A recent study has shown that SARS-CoV-2 infection triggers an imbalance in immune cells called T regulatory cells that are critical to immune balance.
Bacteria from the gut microbiome are responsible for the proper activation of those T-regulatory cells. Thus, researchers like me need to take repeated patient stool, saliva and blood samples over a longer time frame to learn how the altered microbiome observed in COVID-19 patients can modulate COVID-19 disease severity, perhaps by altering the development of the T-regulatory cells.
As a Latina scientist investigating interactions between diet, microbiome and immunity, I must stress the importance of better policies to improve access to healthy foods, which lead to a healthier microbiome. It is also important to design culturally sensitive dietary interventions for Black and Latinx communities. While a good-quality diet might not prevent SARS-CoV-2 infection, it can treat the underlying conditions related to its severity.
[Get our best science, health and technology stories. Sign up for The Conversation’s science newsletter.]![]()
Ana Maldonado-Contreras, Assistant Professor of Microbiology and Physiological Systems, University of Massachusetts Medical School
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
In The News
>WEATHER: Mark Rosenthal's 7-day forecast (:45). High of 41 today in Worcester
>TOP OF THE NEWS
+Noon: Worcester winter weather emergency, parking ban lifted at 5 p.m. Friday
+Noon: It's Friday! Check Dining Out and Bars & Bands before making plans
+Noon: I ate at the first Checkers location in Mass. Here’s what it’s like
+Noon: New shows & movies to watch this weekend
+Noon: New movies on streaming: "Dead Man's Wire," "The Voice of Hind Rajab" and more
-Worcester residents frustrated with snow cleanup: "Florida looks awful freakin’ good"
-Chaos erupts as Worcester officer becomes trapped in car (3:55)
-Worcester Police Department is down nearly 60 officers: "This is a real crisis"
-Worcester police union leader influenced offer in Haxhiaj case, assistant district attorney says
-UMass Memorial transfers transgender patients to new surgeons following abrupt cancellations
-Illegal dumping fines could jump to $1,000 in Worcester
-Worcester School Committee eyes C.R.P., data privacy
-Mass. accuses Barre public employee of double-dipping (3:20). Article
-Trash and recycling delayed by 2 days in Worcester
>DINING OUT: TODAY! Thrive Support and Advocacy fundraiser at 2 Chefs
-ICYMI: Complaint alleges Worcester pastor used investor money for lavish trips
-How many snow days has Worcester had this year? When will school end now?
-Worcester city councilors push for "city with no potholes" dream
-City councilors want police to speed up crackdown on traffic law violators
-Worcester councilor pushes for city investigation of Saint Vincent Hospital
-See the rest of the day's Worcester news
>HOLDEN (brought to you by Lamoureux Ford): Holden police introduce new officer
-Trash and recycling pickup will be delayed a day this week
-Winter snow brings great values at Lamoureux Ford (2:00)
-Jazzed Up Duo at Val’s Friday and Saturday
>THE BURBS (brought to you by North End Motor Sales): Man facing charges for allegedly kidnapping 13-year-old in Northborough
-A new development on Elizabeth Street in Shrewsbury?
-Heavy fire tears through home on Lakeshore Drive in Ashburnham
-2 vehicle rollovers in Grafton amid snowy conditions
-Charlton Select Board begins process to change town's health insurance after steep premium hikes
>BARS & BANDS: The Mayor's Live Music List for Friday
-100 FM The Pike (13:34): Is it a Seger bar? Brian Daly on his viral mission to find out
>SHOWTIME: Things to do: Sugar maples, Chris Fitz in concert, Midori and more ...
-100 FM The Pike (7:14): Worcester's Angelo Gray is making movies and singing his heart out
-Poet's Cauldron to welcome Ursula Rucker at BrickBox Theater
>OPINION: Owura Sarkodieh: In praise of embracing African identity
-Lindsey Ford: 5 practical tips to reset digital habits after winter break
-Holy Cross' Worcester Voices (31:12): Clark Professor Melinda Marchand about her Worcester experience
-What’s Up Worcester (21:43): Dominican Marketplace Committee interview | Jennie Guzman & Laura Martinez
>OBITUARIES: Tribute to Worcester girl who tragically passed away at 13
>SPORTS: A.J. Brown stirs Patriots buzz as trade rumors begin to swirl again
-Bruins beat Columbus, 4-2
-Holy Cross women's ice hockey hosts New Hampshire in Hockey East Quarterfinals
-Worcester Public Schools Athletic Hall Of Fame announces 2026 inductees
-The Olympic break sees many former Worcester pros at the top of their leagues
>NATIONAL: F.B.I. makes final sweep of Nancy Guthrie's house in sign investigation has hit a dead end
-Bikini-clad women pictured with Stephen Hawking in Epstein files were his carers, family claims
-Tragic: Grandfather kidnapped from his bed and murdered in case of mistaken identity, police say
>NEW ENGLAND: Woman, 2-year-old girl recovering after home explosion (1:29)
-Malden High School girls' basketball coach charged with raping student (1:38). Article
>COLLEGES: WPI Podcast, Episode 27 (33:26): A.I. at WPI, with Elke Rundensteiner and Yunus Telliel
-Clark student Skye Donaldson paints mural in Goddard Library to inspire
>TRAVEL (brought to you by Fuller RV & Rental): These 4 popular national parks announce plans for 2026 visitor reservations
-Norwegian Cruise Line slammed over dining dress code change: "Idiotic rule"
>BUSINESS: Twitter founder Jack Dorsey cuts 4,000 jobs from Block in A.I. pivot
-LPL Financial Research: LPL Research’s 2026 strategic asset allocation
-Paramount wins bidding war for Warner Brothers Discovery
>HOMES: Central Mass. home sales slow to start 2026
>HEALTH: "Boredom challenge" could have benefits for your brain (:18)
>FOOD: The pistachio bread recipe you "knead" to try (7:57)
>TV/STREAMING: Anderson Cooper leaving "60 Minutes" in latest CBS staff shakeup
>MOVIES: 25th anniversary trailer for "The Mummy" (:31)
>CELEBRITY: The real reason behind Cardi B and Stefon Diggs' split revealed
-Wu-Tang Clan founding member Oliver "Power" Grant dies at 52
>ANIMALS: Disabled lamb becomes her dad’s wedding ring bearer (1:54)
>HISTORY: Storm comparison: Blizzard of '78 vs. Blizzard of '26 (6:22)
>GOOD NEWS: Kidney donor braves blizzard for Boston transplant surgery (1:52)
-Meanwhile, in Florida, deer crashes into home through living room window
Latest obituaries | | Thursday's Highlights | | Today's horoscope | | Local Sports
Quick Links: Personalize your news | | Browse members | | Advertise | | Blogs | | Invite friends | | Videos
Animals | | Boston Sports | | Business | | Cars | | Celebrity | | Colleges | | Commute & Travel | | Crime | | Faith | | Food | | Good News | | Health | | Help Wanted | History | | Homes | | Local Sports | | Lottery | | Movies | | National | | New England | | Politics | | Shopping & Deals | | SHOWTIME! | | TV & Streaming | | Weather