Make the016.com a preferred choice with Google by clicking here 
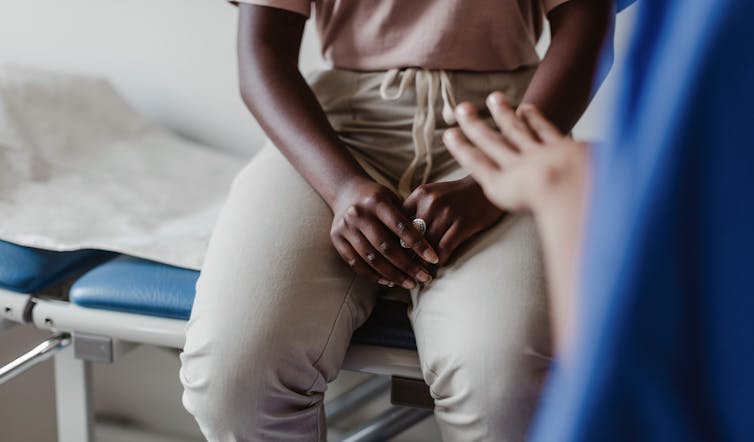
Black patients can be wary of the medical establishment. Maskot via Getty Images
Esther Jones, Clark University
Black Americans have been the least inclined of any racial or ethnic group to say they’d get vaccinated against the coronavirus. The proportion of Black people who said they’ll probably or definitely take the shot has risen over time – but even by mid-January, with two COVID-19 vaccines authorized for emergency use in the U.S., only 35% of Black survey respondents said they’d get it as soon as they could, or already had gotten the shot.
At the same time, the COVID-19 pandemic has disproportionately harmed Black, Indigenous and other people of color in comparison to white members of American society. With Black Americans being hospitalized at rates 2.9 times higher than white Americans and dying from COVID-19 at rates 1.9 times higher, you might assume that Black people would be lining up at breakneck speed to receive the vaccine as soon as it’s available to them.
But the Black community has reasons for distrust – even beyond what might be attributed to the mixed messaging of the nation’s COVID-19 response. And it’s not a simple or sole matter of miseducation. I’m a medical humanist and bioethicist who studies history, ethics and literature to understand racial and gender health disparities. My research explores the history of unethical and abusive treatment Black Americans have experienced at the hands of the medical establishment. Based on past experience, Black people have many legitimate reasons to be in no hurry to get the vaccination.
The American medical establishment has a long history of unethical treatment of Black research subjects. Medical ethicist Harriet A. Washington details some of the most egregious examples in her book “Medical Apartheid.” There’s the now notorious Tuskegee syphilis experiment, in which the government misled Black male patients to believe they were receiving treatment for syphilis when, in fact, they were not. That study went on for a total of 40 years, continuing even after a cure for syphilis was developed in the 1940s.
Perhaps less widely known are the unethical and unjustified experiments J. Marion Sims performed on enslaved women in 1800s U.S. that helped earn him the nickname the “father of modern gynecology.” Sims performed experimental vesicovaginal fistula surgery on enslaved women without anesthesia or even the basic standard of care typical for the time.
Sims experimented on Anarcha, a 17-year-old slave, over 30 times. His decision not to give anesthesia was based on the racist assumption that Black people experience less pain than their white peers – a belief that persists among medical professionals today. Historian Deirdre Cooper Owens elaborates on this case and many other ways Black women’s bodies have been used as guinea pigs in her book “Medical Bondage.”
Cases of medical malfeasance and malevolence have persisted, even after the establishment of the Nuremburg code, a set of medical ethical principles developed after World War II and subsequent trials for crimes against humanity.
A great-granddaughter of Henrietta Lacks poses with her portrait. The HeLa cell line used in medical research originated with a tissue sample from Lacks. Katherine Frey/The Washington Post via Getty Images
In 1951, doctors harvested cervical cancer cells from a Black woman named Henrietta Lacks without her permission. Researchers went on to use them to create the first immortal cell culture and subjected her descendants to ongoing study for years without informed consent. Investigative journalist Rebecca Skloot details the cascade of ethical violations in her book “The Immortal Life of Henrietta Lacks.” Despite heightened awareness after the book’s publication, the ethical violations continued when a group of scientists mapped the HeLa genome without her family’s knowledge or consent.
Advances in genomics are still being used to resuscitate theories of racial “science.” For example, a now-debunked 2007 study purported to isolate a so-called “warrior gene” in Maori Indigenous men and argued they are genetically “hard-wired” for violence. Scientists and news outlets in the U.S. jumped on board, suggesting there’s a genetic predisposition for Black and Latino males to engage in gang activity.
Legal scholar Dorothy E. Roberts explains in her book “Fatal Invention” how incidents like this one perpetuate the harm of race-based science. Using biological data and flawed reasoning tainted by racial stereotyping reinforces racist beliefs about Black people. Such logic focuses on purely biological factors and ignores the social and systemic factors that produce negative and inequitable health outcomes.
While there is now an ample body of scholarly research that reveals these truths about racism in the medical establishment, Black Americans need only to gather around the kitchen table with a few friends and family to share and hear personally experienced stories of medical malfeasance.
Even though their experiences at the hands of researchers like J. Marion Sims were central to advances in modern gynecology, today Black women have not benefited from these advances to the same degree as white women. Black women still suffer worse outcomes and more deaths from gynecologic cancers and have worse health and more deaths affiliated with childbearing, just to name two.
Maternal health and mortality statistics are worse for Black women than their white counterparts. Jose Luis Pelaez Inc/DigitalVision via Getty Images
When tennis star Serena Williams gave birth, she saw firsthand how Black women are disbelieved by the medical establishment. She might have died from postpartum blood clots if she hadn’t advocated for herself in the face of dismissive medical professionals.
[Get our best science, health and technology stories. Sign up for The Conversation’s science newsletter.]
Black people are acutely aware of this history of racism in the medical establishment, and the ways it persists today on both an individual and a collective level. Stereotypes about Black patients, whether the result of explicit or implicit bias, continue to affect the care they receive and their medical outcomes. Again and again, when surveyed, Black Americans report that medical providers don’t believe them, won’t prescribe necessary treatments, including pain medication, and blame them for their health problems.
And the association between racism and increased disease cases and deaths has held true during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Ongoing trust issues around the COVID-19 vaccines are just the latest indication of racial health disparities in the U.S.
Still, there are ways to begin to close the COVID-19 racial health and mortality gap. Vaccinations for Black people may otherwise continue to lag in proportion to population size.
An important first step is for health care workers and policymakers to learn these painful histories and develop strategies informed by an understanding of the systemic racism Black Americans face.![]()
Esther Jones, Associate Professor of English, affiliate with Africana Studies and Women's & Gender Studies, Clark University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
In The News
>WEATHER: Mark Rosenthal's 7-day forecast (:45). High of 41 today in Worcester
>TOP OF THE NEWS
+Noon: Worcester winter weather emergency, parking ban lifted at 5 p.m. Friday
+Noon: It's Friday! Check Dining Out and Bars & Bands before making plans
+Noon: I ate at the first Checkers location in Mass. Here’s what it’s like
+Noon: New shows & movies to watch this weekend
+Noon: New movies on streaming: "Dead Man's Wire," "The Voice of Hind Rajab" and more
-Worcester residents frustrated with snow cleanup: "Florida looks awful freakin’ good"
-Chaos erupts as Worcester officer becomes trapped in car (3:55)
-Worcester Police Department is down nearly 60 officers: "This is a real crisis"
-Worcester police union leader influenced offer in Haxhiaj case, assistant district attorney says
-UMass Memorial transfers transgender patients to new surgeons following abrupt cancellations
-Illegal dumping fines could jump to $1,000 in Worcester
-Worcester School Committee eyes C.R.P., data privacy
-Mass. accuses Barre public employee of double-dipping (3:20). Article
-Trash and recycling delayed by 2 days in Worcester
>DINING OUT: TODAY! Thrive Support and Advocacy fundraiser at 2 Chefs
-ICYMI: Complaint alleges Worcester pastor used investor money for lavish trips
-How many snow days has Worcester had this year? When will school end now?
-Worcester city councilors push for "city with no potholes" dream
-City councilors want police to speed up crackdown on traffic law violators
-Worcester councilor pushes for city investigation of Saint Vincent Hospital
-See the rest of the day's Worcester news
>HOLDEN (brought to you by Lamoureux Ford): Holden police introduce new officer
-Trash and recycling pickup will be delayed a day this week
-Winter snow brings great values at Lamoureux Ford (2:00)
-Jazzed Up Duo at Val’s Friday and Saturday
>THE BURBS (brought to you by North End Motor Sales): Man facing charges for allegedly kidnapping 13-year-old in Northborough
-A new development on Elizabeth Street in Shrewsbury?
-Heavy fire tears through home on Lakeshore Drive in Ashburnham
-2 vehicle rollovers in Grafton amid snowy conditions
-Charlton Select Board begins process to change town's health insurance after steep premium hikes
>BARS & BANDS: The Mayor's Live Music List for Friday
-100 FM The Pike (13:34): Is it a Seger bar? Brian Daly on his viral mission to find out
>SHOWTIME: Things to do: Sugar maples, Chris Fitz in concert, Midori and more ...
-100 FM The Pike (7:14): Worcester's Angelo Gray is making movies and singing his heart out
-Poet's Cauldron to welcome Ursula Rucker at BrickBox Theater
>OPINION: Owura Sarkodieh: In praise of embracing African identity
-Lindsey Ford: 5 practical tips to reset digital habits after winter break
-Holy Cross' Worcester Voices (31:12): Clark Professor Melinda Marchand about her Worcester experience
-What’s Up Worcester (21:43): Dominican Marketplace Committee interview | Jennie Guzman & Laura Martinez
>OBITUARIES: Tribute to Worcester girl who tragically passed away at 13
>SPORTS: A.J. Brown stirs Patriots buzz as trade rumors begin to swirl again
-Bruins beat Columbus, 4-2
-Holy Cross women's ice hockey hosts New Hampshire in Hockey East Quarterfinals
-Worcester Public Schools Athletic Hall Of Fame announces 2026 inductees
-The Olympic break sees many former Worcester pros at the top of their leagues
>NATIONAL: F.B.I. makes final sweep of Nancy Guthrie's house in sign investigation has hit a dead end
-Bikini-clad women pictured with Stephen Hawking in Epstein files were his carers, family claims
-Tragic: Grandfather kidnapped from his bed and murdered in case of mistaken identity, police say
>NEW ENGLAND: Woman, 2-year-old girl recovering after home explosion (1:29)
-Malden High School girls' basketball coach charged with raping student (1:38). Article
>COLLEGES: WPI Podcast, Episode 27 (33:26): A.I. at WPI, with Elke Rundensteiner and Yunus Telliel
-Clark student Skye Donaldson paints mural in Goddard Library to inspire
>TRAVEL (brought to you by Fuller RV & Rental): These 4 popular national parks announce plans for 2026 visitor reservations
-Norwegian Cruise Line slammed over dining dress code change: "Idiotic rule"
>BUSINESS: Twitter founder Jack Dorsey cuts 4,000 jobs from Block in A.I. pivot
-LPL Financial Research: LPL Research’s 2026 strategic asset allocation
-Paramount wins bidding war for Warner Brothers Discovery
>HOMES: Central Mass. home sales slow to start 2026
>HEALTH: "Boredom challenge" could have benefits for your brain (:18)
>FOOD: The pistachio bread recipe you "knead" to try (7:57)
>TV/STREAMING: Anderson Cooper leaving "60 Minutes" in latest CBS staff shakeup
>MOVIES: 25th anniversary trailer for "The Mummy" (:31)
>CELEBRITY: The real reason behind Cardi B and Stefon Diggs' split revealed
-Wu-Tang Clan founding member Oliver "Power" Grant dies at 52
>ANIMALS: Disabled lamb becomes her dad’s wedding ring bearer (1:54)
>HISTORY: Storm comparison: Blizzard of '78 vs. Blizzard of '26 (6:22)
>GOOD NEWS: Kidney donor braves blizzard for Boston transplant surgery (1:52)
-Meanwhile, in Florida, deer crashes into home through living room window
Latest obituaries | | Thursday's Highlights | | Today's horoscope | | Local Sports
Quick Links: Personalize your news | | Browse members | | Advertise | | Blogs | | Invite friends | | Videos
Animals | | Boston Sports | | Business | | Cars | | Celebrity | | Colleges | | Commute & Travel | | Crime | | Faith | | Food | | Good News | | Health | | Help Wanted | History | | Homes | | Local Sports | | Lottery | | Movies | | National | | New England | | Politics | | Shopping & Deals | | SHOWTIME! | | TV & Streaming | | Weather